NASA Astronomy Picture of the Day:
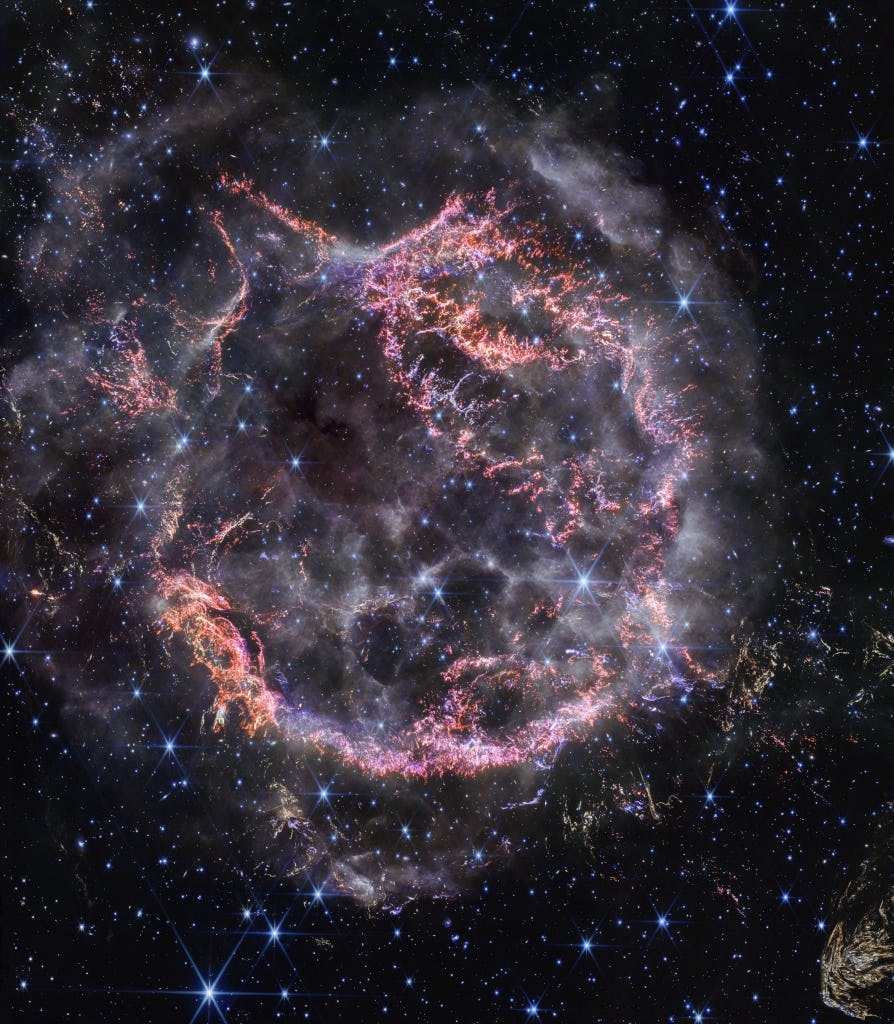
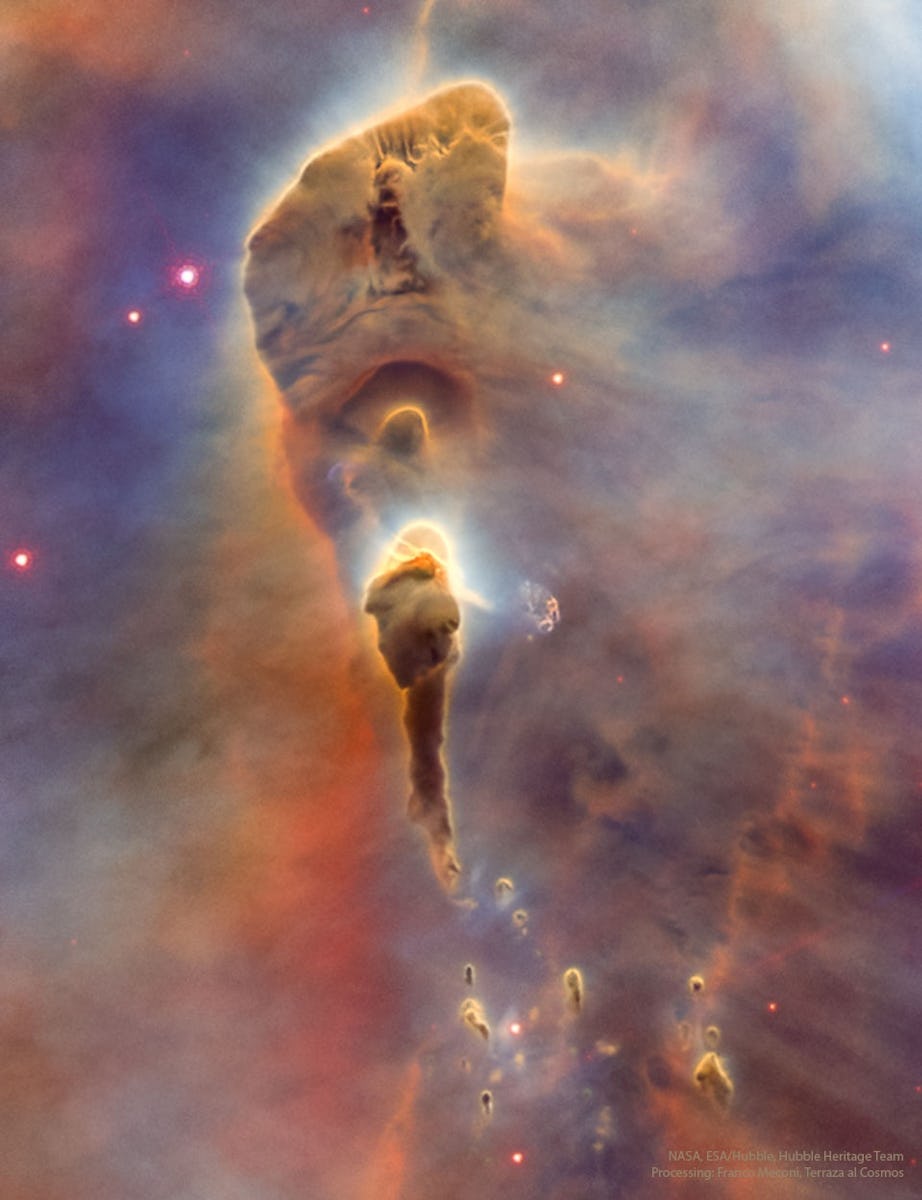
Massive stars in our Milky Way Galaxy live spectacular lives. Collapsing from vast cosmic clouds, their nuclear furnaces ignite and create heavy elements in their cores. After only a few million years for the most massive stars, the enriched material is blasted back into interstellar space where star formation can begin anew. The expanding debris cloud known as Cassiopeia A is an example of this final phase of the stellar life cycle. Light from the supernova explosion that created this remnant would have been first seen in planet Earth's sky about 350 years ago, although it took that light 11,000 years to reach us. This sharp NIRCam image from the James Webb Space Telescope shows the still hot filaments and knots in the supernova remnant. The whitish, smoke-like outer shell of the expanding blast wave is about 20 light-years across. Light echoes from the massive star's cataclysmic explosion are also identified in Webb's detailed image of supernova remnant Cassiopeia A. Tonight watch: The Geminids








.jpg?fit=crop&w=280&h=280&q=93)